
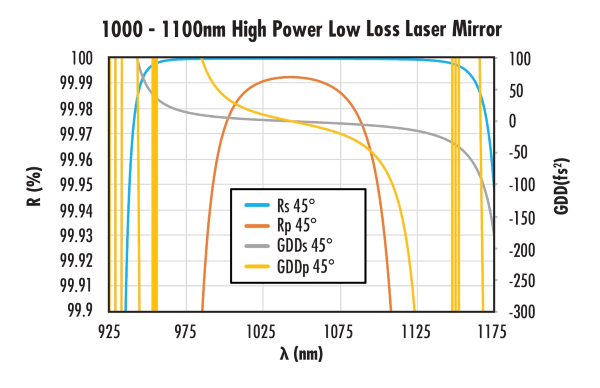
UltraFast Innovations (UFI) High-Power Low-Loss Laser Mirrors provide >99.99% reflectivity with industry leading damage thresholds. Laser grade surface quality and surface flatness with 0fs2 group delay dispersion (GDD) at 1030nm and 1064nm make these mirrors ideal for the requirements of demanding laser applications. With >99.99% reflectivity of s-polarized light and >99.98% reflectivity of p-polarized light, these mirrors can be used with nanosecond, picosecond, and femtosecond lasers. Durable dielectric coatings are tested to ensure a high laser damage threshold of >50 J/cm2 at 1064nm, 100Hz, 8ns. UFI High-Power Low-Loss Laser Mirrors feature fused silica substrates with excellent thermal stability and a 25.4mm diameter to facilitate integration into 1030nm or 1064nm laser systems. Please contact us if your application requires a High Power Low Loss Laser Mirror with a custom size or coating.
1-800-363-1992
or view regional numbers
QUOTE TOOL
enter stock numbers to begin
Copyright 2025, Edmund Optics Inc., 101 East Gloucester Pike, Barrington, NJ 08007-1380 USA
California Consumer Privacy Acts (CCPA): Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
California Transparency in Supply Chains Act